
판다스 공식 홈페이지
pandas - Python Data Analysis Library
pandas pandas is a fast, powerful, flexible and easy to use open source data analysis and manipulation tool, built on top of the Python programming language. Install pandas now!
pandas.pydata.org
데이터 활용 공모전 준비와
인공지능(AI)에 필요한 머신러닝을 익히기 위해 우선 데이터 분석을 공부하게 되었다.
판다스를 배우는 이유
- 데이터 분석에서는 데이터 자체가 가장 중요한 자원이다.
- 실제로 데이터 분석 업무의 80% ~ 90%는 데이터를 수집하고 정리하는 일이다.
- 나머지 10%~20%는 알고리즘 선택하고 모델링 결과를 분석하여 데이터로부터 유용한 정보를 뽑아내는 일
- 판다스 라이브러리는 데이터를 수집하고 정리하는 데 최적화된 도구이다.
판다스 자료구조
- 판다스는 시리즈(Series)와 데이터프레임(DataFrame)이라는 구조화된 데이터 형식을 제공
- 판다스 라이브러리는 여러 종류의 클래스와 다양한 내장 함수로 구성
- 시리즈와 데이터프레임은 데이터 구조를 표현하는 대표적인 클래스 객체
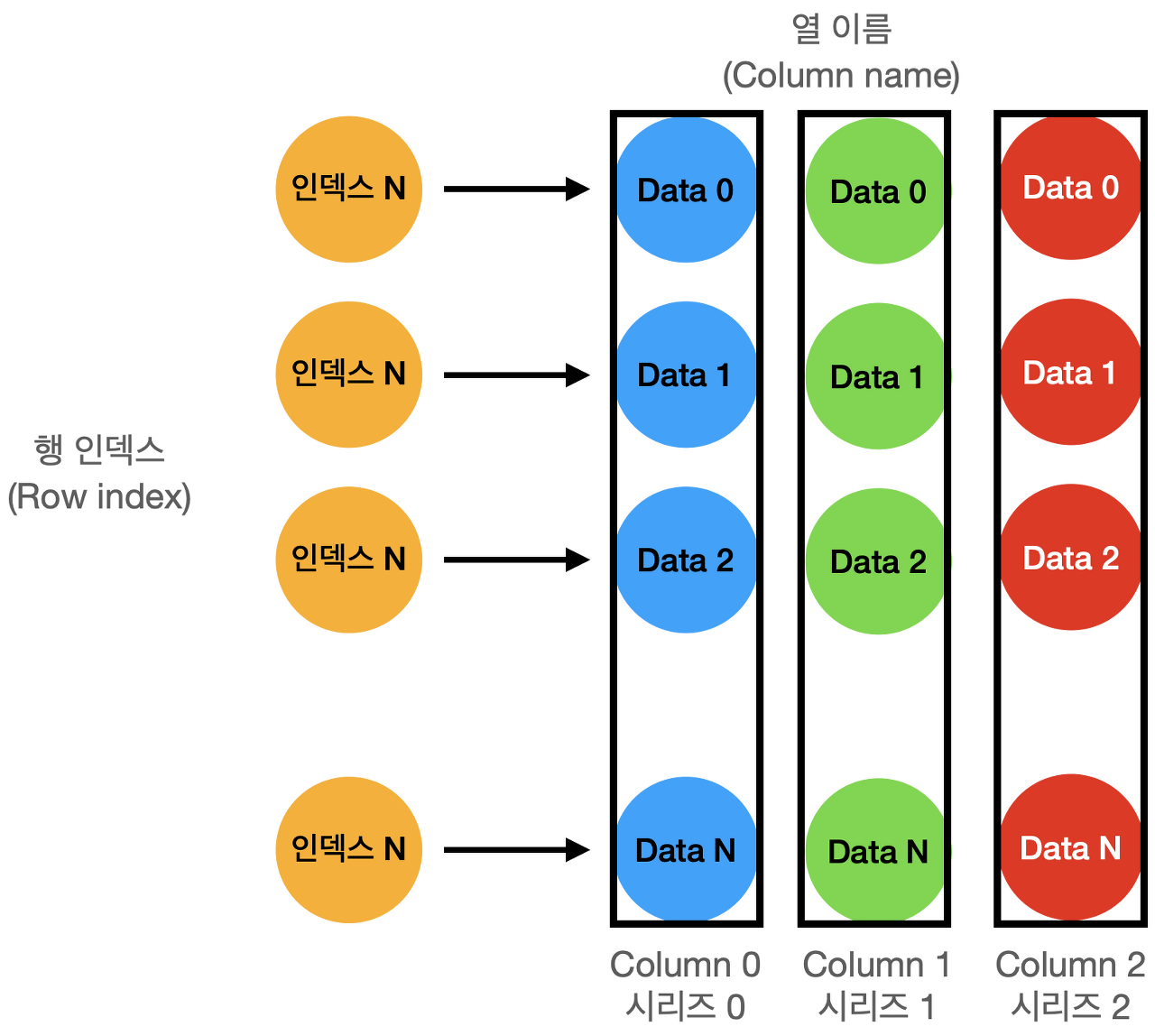

시리즈(Series)
시리즈는 데이터가 순차적으로 나열된 1차원 배열의 형태를 갖는다.
ex) 딕셔너리 -> 시리즈 변환
# 딕셔너리 -> 시리즈변환
import pandas as pd
dict_data = {'a':1, 'b':2,'c':3}
sr = pd.Series(dict_data)
print(type(sr))
sr<결과>
<class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
a 1
b 2
c 3
dtype: int64
ex) 리스트 -> 시리즈 변환
# 리스트 -> 시리즈 변환 / 인덱스 설정
list_data = ['2021-06-30',3.14,'ABC',100,True]
sr = pd.Series(list_data, index=['날짜','파이','영어','일백','부울'])
sr<결과>
날짜 2021-06-30
파이 3.14
영어 ABC
일백 100
부울 True
dtype: object
.index .values
# index 와 values
print(sr.index)
print(sr.values)<결과>
Index(['날짜', '부울', '파이', '영어', '일백'], dtype='object')
['2021-06-30' 3.14 'ABC' 100 True]
인덱스에는 크게 두 가지 종류가 있다
정수형 위치 인덱스, 인덱스 이름
# 튜플 -> 시리즈
tup_data = ('철수','2021-06-30','남',True)
tsr = pd.Series(tup_data, index=['이름','생년월일','성별','학생여부'])
tsr<결과>
이름 철수
생년월일 2021-06-30
성별 남
학생여부 True
dtype: object
인덱스 활용
# 인덱스 활용
print(tsr[0])
print()
print(tsr['이름'])
print()
# 다중값
print(tsr[[1,2]])
print()
print(tsr[['생년월일','성별']])<결과>
철수
철수
생년월일 2021-06-30
성별 남
dtype: object
생년월일 2021-06-30
성별 남
dtype: object
슬라이싱
# 슬라이싱
print(tsr[1:2]) # 인덱스 1~ (2-1)
print()
print(tsr['학생여부':'성별'])<결과>
생년월일 2021-06-30
dtype: object
Series([], dtype: object)
데이터프레임
딕셔너리 -> 데이터프레임
# 데이터프레임 p11
## 딕셔너리 -> 데이터프레임
dict_data= {'c0':[1,2,3], 'c1':[4,5,6], 'c2':[7,8,9], 'c3':[10,11,12], 'c4':[13,14,15]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict_data)
print(type(df))
df<결과>
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
c0 c1 c2 c3 c4
0 1 4 7 10 13
1 2 5 8 11 14
2 3 6 9 12 15
pandas.DataFrame(2 차원배열
index=행 인덱스 배열 , columns=열 이름 배열)
행인덱스/열이름 지정하여, 데이터프레임 만들기
df = pd.DataFrame([[15, '남', '덕영중'], [17, '여', '수리중']],
index=['준서', '예은'],
columns=['나이', '성별', '학교'])
print(df.index)
print(df.columns)
df<결과>
Index(['준서', '예은'], dtype='object')
Index(['나이', '성별', '학교'], dtype='object')
나이 성별 학교
준서 15 남 덕영중
예은 17 여 수리중
행 인덱스, 열 이름 변경하기
..위 결과를 이어
# 행 인덱스 , 열 이름 변경하기
df.index=['학생1','학생2']
df.columns=['연령','남녀','소속']
df<결과>
연령 남녀 소속
학생1 15 남 덕영중
학생2 17 여 수리중
rename 함수
..위 결과를 이어
# rename 함수
print(df)
df.rename(columns={'연령':'Age','남녀':'Sex','소속':'School'},inplace=True)
df.rename(index={'학생1':'철수', '학생2':'영희'},inplace=True)
df<결과>
Age Sex School
철수 15 남 덕영중
영희 17 여 수리중
삭제
행 삭제 예제
# 행 삭제 예제
## DataFrame() 함수로데이터프레임변환. 변수df에저장
exam_data= {'수학' : [ 90, 80, 70], '영어' : [ 98, 89, 95],'음악' : [ 85, 95, 100], '체육' : [ 100, 90, 90]}
exam_df = pd.DataFrame(exam_data, index=['박서준','박보영','서인국'])
print(exam_df)
# 1개 행 삭제
df2 = exam_df[:]
df2.drop('박서준',inplace=True)
print(df2)
print()
# 2개 행 삭제
df3 = exam_df[:]
df3.drop(['박보영','서인국'],axis=0, inplace=True)
df3<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육
박서준 90 98 85 100
박보영 80 89 95 90
서인국 70 95 100 90
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 80 89 95 90
서인국 70 95 100 90
수학 영어 음악 체육
박서준 90 98 85 100
열 삭제 예제
# 열 삭제 예제
# DataFrame() 함수로데이터프레임변환. 변수df에저장
exam_data= {'수학' : [ 90, 80, 70], '영어' : [ 98, 89, 95],'음악' : [ 85, 95, 100], '체육' : [ 100, 90, 90]}
score_df = pd.DataFrame(exam_data, index=['박보영','서인국','멸망'])
print(score_df)
print()
# 1개 열 삭제
sdf1 = score_df[:]
sdf1.drop('수학',axis=1,inplace=True)
print(sdf1)
print()
sdf2 = score_df[:]
sdf2.drop(['영어','음악'],axis=1,inplace=True)
print(sdf2)<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 90 98 85 100
서인국 80 89 95 90
멸망 70 95 100 90
영어 음악 체육
박보영 98 85 100
서인국 89 95 90
멸망 95 100 90
수학 체육
박보영 90 100
서인국 80 90
멸망 70 90
행 선택
loc, iloc
# 행 선택 , loc, iloc
print(score_df)
print()
## 행 1개 선택
park_series = score_df.loc['박보영']
p_series = score_df.iloc[0]
print(park_series, type(park))
print()
print(p_series)
<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 90 98 85 100
서인국 80 89 95 90
멸망 70 95 100 90
수학 90
영어 98
음악 85
체육 100
Name: 박보영, dtype: int64 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
수학 90
영어 98
음악 85
체육 100
Name: 박보영, dtype: int64
행 2개 이상 선택
# 행 2개 이상 선택
print(score_df)
print(score_df.loc[['박보영','서인국']])
print(score_df.iloc[[0,1]])<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 90 98 85 100
서인국 80 89 95 90
멸망 70 95 100 90
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 90 98 85 100
서인국 80 89 95 90
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 90 98 85 100
서인국 80 89 95 90
행과 열 지정
df.iloc[:,[0,1]]
불린 인덱싱
changed_df_=changed_df['add'].isin([32.0, 48.0])
print(df.loc[changed_df_,:])
print(df[changed_df_])
# 여러 조건 일경우
print(df[fun1 | func2 | func3])
열 재구성 | 열 순서 변경
col_list = ['ten','fare','age','add']
changed_df = df[col_list]
슬라이싱
# 슬라이싱
print(score_df)
print(score_df.loc['박보영':'서인국'])
print(score_df.iloc[0:1])
print(score_df.iloc[::-1]) # 행 역순<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 90 98 85 100
서인국 80 89 95 90
멸망 70 95 100 90
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 90 98 85 100
서인국 80 89 95 90
수학 영어 음악 체육
박보영 90 98 85 100
수학 영어 음악 체육
멸망 70 95 100 90
서인국 80 89 95 90
박보영 90 98 85 100
한 점(결과 값)
# 한 점의 값
a = score_df.loc['멸망','수학']
print(a, type(a))
print(score_df.iloc[0,2], type(score_df.iloc[0,2]))
print()
# 한행, 여러 컬럼 -> 시리즈
print(score_df.loc['박보영',['수학','영어']], type(score_df.loc['박보영',['수학','영어']]))
print(score_df.loc['박보영', '수학':'영어'])
print(score_df.iloc[0,[0,1]])
print(score_df.iloc[0, 2:]) # 음악 ,체육
print()
# 데이터프레임의 행 인덱스와 열 이름을 [행, 열] 형식의 2 차원 좌표로 입력 -> 데이터프레임 객체 반환
print(score_df.iloc[[0,1],[1,2]])
print(type(score_df.iloc[[0,1],[1,2]]))
print(score_df.iloc[0:2, 1:3])
<결과>
#한 점의 값
70 <class 'numpy.int64'>
85 <class 'numpy.int64'>
#한 행, 여러 컬럼 -> 시리즈
수학 90
영어 98
Name: 박보영, dtype: int64 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
수학 90
영어 98
Name: 박보영, dtype: int64
수학 90
영어 98
Name: 박보영, dtype: int64
음악 85
체육 100
Name: 박보영, dtype: int64
# 데이터프레임의 행 인덱스와 열 이름을 [행, 열] 형식의 2 차원 좌표로 입력 -> 데이터프레임 객체 반환
영어 음악
박보영 98 85
서인국 89 95
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
영어 음악
박보영 98 85
서인국 89 95
열 선택
# 열 선택 #
exam_data= {
'이름' : [ '서준', '우현', '인아'],
'수학' : [ 90, 80, 70],
'영어' : [ 98, 89, 95],
'음악' : [ 85, 95, 100],
'체육' : [ 100, 90, 90]
}
df=pd.DataFrame(exam_data)
df.set_index('이름',inplace=True)
df
math1 = df['수학']
print(math1, type(math1))
eng1 = df.영어
print(eng1, type(eng1))
# 이중 대괄호로 할경우 데이터프레임 반환
music_gym = df[['음악','체육']]
print(music_gym,type(music_gym))
math2 = df[['수학']]
print(math2, type(math2))
<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육
이름
서준 90 98 85 100
우현 80 89 95 90
인아 70 95 100 90
이름
서준 90
우현 80
인아 70
Name: 수학, dtype: int64 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
이름
서준 98
우현 89
인아 95
Name: 영어, dtype: int64 <class 'pandas.core.series.Series'>
# 이중 대괄호로 할경우 데이터프레임 반환
음악 체육
이름
서준 85 100
우현 95 90
인아 100 90 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
수학
이름
서준 90
우현 80
인아 70 <class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
열 추가
# 단일 값으로 추가
exam_data= {
'이름' : [ '서준', '우현', '인아'],
'수학' : [ 90, 80, 70],
'영어' : [ 98, 89, 95],
'음악' : [ 85, 95, 100],
'체육' : [ 100, 90, 90]
}
df=pd.DataFrame(exam_data)
df['국어'] = 80
행 추가
df.loc[3]= 0
print(df,'\n')
df.loc[4] = ['동규',10,20,30,40,50]
print(df,'\n')
df.loc[5] = df.loc[3]
print(df)<결과>
기존
수학 영어 음악 체육
이름
서준 90 98 85 100
우현 80 89 95 90
인아 70 95 100 90
이름 수학 영어 음악 체육 국어
0 서준 90 98 85 100 80
1 우현 80 89 95 90 80
2 인아 70 95 100 90 80
3 0 0 0 0 0 0
이름 수학 영어 음악 체육 국어
0 서준 90 98 85 100 80
1 우현 80 89 95 90 80
2 인아 70 95 100 90 80
3 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 동규 10 20 30 40 50
이름 수학 영어 음악 체육 국어
0 서준 90 98 85 100 80
1 우현 80 89 95 90 80
2 인아 70 95 100 90 80
3 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 동규 10 20 30 40 50
5 0 0 0 0 0 0
원소 값 변경
df.set_index('이름',inplace=True)
df.iloc[0][3] = 80
df.loc['서준']['체육'] = 80
df.loc['서준','체육'] = 90
df.loc['우현',['체육','국어']] = 100, 100
print(df)<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육 국어
이름
서준 90 98 85 90 80
우현 80 89 95 100 100
인아 70 95 100 90 80
0 0 0 0 0 0
동규 10 20 30 40 50
0 0 0 0 0 0
열 전체 변경
ndf.loc[ndf['mpg']>= 18,'mpg']= 1
ndf<결과>
mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight acceleration model year origin name kpl hp_name 저출력 보통출력 고출력
0 1.0 8 307.0 130.0 3504.0 12.0 70 USA chevrolet chevelle malibu 7.65 보통출력 0 1 0
1 15.0 8 350.0 165.0 3693.0 11.5 70 USA buick skylark 320 6.38 보통출력 0 1 0
2 1.0 8 318.0 150.0 3436.0 11.0 70 USA plymouth satellite 7.65 보통출력 0 1 0
행과 열 바꾸기 = 전치
# 행과 열 바꾸기, 전치
exam_data= {
'이름' : [ '서준', '우현', '인아'],
'수학' : [ 90, 80, 70],
'영어' : [ 98, 89, 95],
'음악' : [ 85, 95, 100],
'체육' : [ 100, 90, 90]
}
df= pd.DataFrame(exam_data)
print(df,'\n')
print(df.T)<결과>
이름 수학 영어 음악 체육
0 서준 90 98 85 100
1 우현 80 89 95 90
2 인아 70 95 100 90
0 1 2
이름 서준 우현 인아
수학 90 80 70
영어 98 89 95
음악 85 95 100
체육 100 90 90
정렬
# 내림차순 인덱스 정렬 #
df.set_index('이름')
print(df.sort_index(ascending=False),'\n')
# 컬럼 하나를 기준으로 값 정렬 #
print(df.sort_values(by='수학',ascending=False))<결과>
이름 수학 영어 음악 체육
2 인아 70 95 100 90
1 우현 80 89 95 90
0 서준 90 98 85 100
이름 수학 영어 음악 체육
0 서준 90 98 85 100
1 우현 80 89 95 90
2 인아 70 95 100 90
산술 연산
# 산술 연산 #
## 시리즈 연산
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
student1 = pd.Series({'국어':np.nan, '영어':80, '수학':90})
student2 = pd.Series({'수학':80, '국어':90})
print(student1)
print(student2)<결과>
국어 NaN
영어 80.0
수학 90.0
dtype: float64
수학 80
국어 90
dtype: int64
NaN 값 -> 0 으로 채우기
# NaN 값 -> 0 으로 채우기
sr_add = student1.add(student2, fill_value=0)
sr_sub = student1.sub(student2, fill_value=0)
sr_mul = student1.mul(student2, fill_value=0)
sr_div = student1.div(student2, fill_value=0)
result = pd.DataFrame([sr_add, sr_sub, sr_mul, sr_div], index=['덧셈','뺄셈','곱셈','나눗셈'])
result<결과>
국어 수학 영어
덧셈 90.0 170.000 80.0
뺄셈 -90.0 10.000 80.0
곱셈 0.0 7200.000 0.0
나눗셈 0.0 1.125 inf
데이터프레임 + 숫자
# 데이터프레임 + 숫자
import seaborn as sns
titanic = sns.load_dataset('titanic')
tit_df = titanic.loc[:,['age','fare']]
print(tit_df.head(),'\n')
add_df = tit_df + 10
print(add_df.head(),'\n')
sub_df = add_df - tit_df
print(sub_df.tail())<결과>
age fare
0 22.0 7.2500
1 38.0 71.2833
2 26.0 7.9250
3 35.0 53.1000
4 35.0 8.0500
age fare
0 32.0 17.2500
1 48.0 81.2833
2 36.0 17.9250
3 45.0 63.1000
4 45.0 18.0500
age fare
886 10.0 10.0
887 10.0 10.0
888 NaN 10.0
889 10.0 10.0
890 10.0 10.0
행 인덱스 재배열
행 인덱스를 새로운 배열로 재지정
dict_data={
'c0':[1,2,3],
'c1':[4,5,6],
'c2':[7,8,9],
'c3':[10,11,12],
}
df= pd.DataFrame(dict_data,index={'r0','r1','r2'})
df
new_index = {'r0','r1','r2','r3','r4'}
ndf= df.reindex(new_index)
ndf
ndf2 = df.reindex(new_index,fill_value=0)
ndf2<결과>
기존 데이터
c0 c1 c2 c3
r0 1 4 7 10
r2 2 5 8 11
r1 3 6 9 12
ndf
c0 c1 c2 c3
r2 2.0 5.0 8.0 11.0
r0 1.0 4.0 7.0 10.0
r4 NaN NaN NaN NaN
r1 3.0 6.0 9.0 12.0
r3 NaN NaN NaN NaN
ndf2
c0 c1 c2 c3
r2 2 5 8 11
r0 1 4 7 10
r4 0 0 0 0
r1 3 6 9 12
r3 0 0 0 0
행 인덱스 초기화
행 인덱스를 정수형 위치 인덱스로 초기화
dict_data={
'c0':[1,2,3],
'c1':[4,5,6],
'c2':[7,8,9],
'c3':[10,11,12],
'c4':[13,14,15]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict_data,index={'r0','r1','r2'})
df
ndf = df.reset_index()
ndf<결과>
기존
c0 c1 c2 c3 c4
r0 1 4 7 10 13
r2 2 5 8 11 14
r1 3 6 9 12 15
ndf
index c0 c1 c2 c3 c4
0 r0 1 4 7 10 13
1 r2 2 5 8 11 14
2 r1 3 6 9 12 15
데이터프레임 연산
함수 적용
exam_data= {'수학' : [ 90, 80, 70],
'영어' : [ 98, 89, 95],
'음악' : [ 85, 95, 100],
'체육' : [ 100, 90, 90]}
df = pd.DataFrame(exam_data, index=['서준', '우현', '인아'])
print(df)
print('\n')
df['수학2'] = df['수학']+5
print(df)
print('\n')
df['총점'] = df['수학'] + df['영어'] + df['음악'] + df['체육']
df['평균'] = df['총점']/4
df
<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육
서준 90 98 85 100
우현 80 89 95 90
인아 70 95 100 90
수학 영어 음악 체육 수학2
서준 90 98 85 100 95
우현 80 89 95 90 85
인아 70 95 100 90 75
수학 영어 음악 체육 수학2 총점 평균
서준 90 98 85 100 95 373 93.25
우현 80 89 95 90 85 354 88.50
인아 70 95 100 90 75 355 88.75
조건식 적용
grades = []
for row in df['평균']:
if row >= 90:
grades.append('A')
elif row >= 80:
grades.append('B')
else:
grades.append('C')
df['성적'] = grades
df
def scholarship(row):
print(row)
if row == 'A':
return '장학생'
else:
return '비장학생'
df.성적 = df.성적.apply(scholarship)
df<결과>
수학 영어 음악 체육 수학2 총점 평균 성적
서준 90 98 85 100 95 373 93.25 장학생
우현 80 89 95 90 85 354 88.50 비장학생
인아 70 95 100 90 75 355 88.75 비장학생
'파이썬 머신러닝 판다스 데이터 분석' 책을 참고하였다.
파이썬 머신러닝 판다스 데이터 분석
데이터 과학자가 되기 위한 첫걸음!파이썬 초급자나 중급자가 데이터 분석과 머신러닝을 배우고자 마음먹었다면 이 책을 선택해야 한다. 필수 라이브러리를 소개하고 설치부터 예제 코드를 따
book.naver.com
'Language > 파이썬' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 파이썬 '판다스 데이터 분석' - 데이터프레임 구조(shape, info(),describe(),value_counts()..), 통계함수(mean(), median(), min(), max(), std(), corr()) (0) | 2021.07.08 |
|---|---|
| 파이썬 '판다스 데이터 분석' - 엑셀 파일 읽기 (xlsx, csv), 여러 엑셀 파일 읽기,캐글 제출을 위한 DataFrame (1) | 2021.07.05 |
| 파이썬을 이용한 OpenCV (0) | 2021.01.31 |
| 파이썬 크롤링, 스크롤링 / python crawling (0) | 2020.07.14 |
| 파이썬 코드 정리 업데이트 할것 (0) | 2020.07.11 |




댓글